Present Perfect. When to use it and can you do without it?

When studying the system of tenses in English, at some point you face a sentence in the Present Perfect Tense. Let's look in detail at this tense, how it is formed, and when it should be used.
The Present Perfect is used to talk about past events and actions that have a connection with the present.
The Formation of the Present Perfect
To get acquainted with the rules for forming the Present Perfect Tense let’s look at the sentence below:
- We have visited many countries.
The subject we is followed by the predicate have visited. Thus, the Present Perfect is formed with the help of the auxiliary verb to have, which changes depending on the person (I/you/we/they have; he/she/it has), and the Past Participle of the main verb. The Past Participle form is formed by adding the ending -ed to the base form of regular verbs. For irregular verbs, we use special third forms (V3), which can be found in the list of irregular verbs.
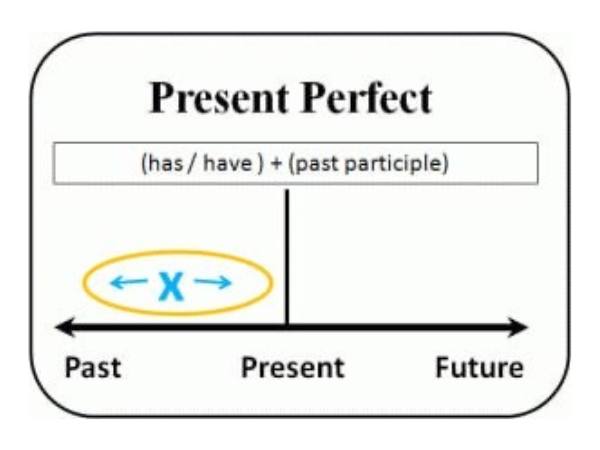
In the tables below, let’s consider in more detail how to use the Present Perfect Simple in positive and negative sentences, questions, and short answers.
|
Positive (+) |
Negative (–) |
|
Subject + have/has +V3 |
Subject + have/has + NOT +V3 |
|
I have cooked pizza |
I have not cooked pizza |
|
You have cooked pizza |
You have not cooked pizza |
|
He has cooked pizza |
He has not cooked pizza |
|
We have cooked pizza |
We have not cooked pizza |
|
You have cooked pizza |
You have not cooked pizza |
|
They have cooked pizza |
They have not cooked pizza |
In order to create a negative sentence in the Present Perfect we use the negative particle not after the auxiliary verb have / has.
|
Question (?) |
Short answer |
|
Have/has + subject + V3 |
Yes, subject + have/has No, subject + have/has + NOT |
|
Have I cooked pizza? |
Yes, I have. No, I have not. |
|
Have you cooked pizza? |
Yes, you have. No, you have not. |
|
Has he cooked pizza? |
Yes, he has. No, he has not. |
|
Have we cooked pizza? |
Yes, we have. No, we have not. |
|
Have you cooked pizza? |
Yes, you have. No, you have not. |
|
Have they cooked pizza? |
Yes, they have. No, they have not. |
To create a yes/no question in the Present Perfect, put the auxiliary verb have/has to the first place, then use subject + V3.
In special questions we use a special question word and then the common structure of a general question: the auxiliary verb have/has + subject + V3.
- Positive (+): He has cooked pizza.
- General ?: Has he cooked pizza?
- Special ?: What has he cooked?
In the tables above we can see the full forms of the Present Perfect Tense, but the contractions are used very often:
|
Positive (+) |
Negative (–) |
|
|
Note! In positive short answers use the full form only, not the contracted one: Has he cooked pizza? - Yes, he has. No he hasn’t (= has not).
The Use of Present Perfect
1. Use the Present Perfect Tense to talk about life experiences, recent news, or events:
- I know this book. I have read it. – (Life experience).
- I have been to many countries. – (Life experience).
- We have changed all the furniture at home. Now it’s different. – (Recent events).
2. The Present Perfect is also used to express unfinished actions:
- Henry has read 50 pages of this book. He says it’s very interesting.
- I have lived in France for 5 months.
- She speaks German. She has studied it for many years.
With the Present Perfect Tense we often use the following marker words expressing an inexact time or incomplete period of time:
- just
- already (in positive sentences)
- yet (in questions and negatives)
- ever
- never
- so far
- recently
- lately
- once
- many (several, a few) times
- before
- today
- this week (month, year)
- this morning
- for a day (week, month, year)
- since last week (month, year)
When studying the Present Perfect, be sure to pay attention to the time markers mentioned above, they indicate when the Present Perfect should be used. If there are no markers, try to understand whether the action is connected to the present. If it is, don’t hesitate to use the Present Perfect.
In English, it is very common to talk about situations where the result of an action that happened is important, while exactly when it happened usually doesn’t matter. For example, he has lost his wallet. Here, what matters is not when it happened, but that he cannot pay for anything right now because he is without his wallet. So, if you are just starting to learn English, to make it easier, you can temporarily use the Past Simple tense for past actions, indicating the time. However, as you advance, be sure to use the Present Perfect, as it is an indispensable tense if you want to sound natural.
The Present Perfect is often used in English and there is no chance we can avoid using it.
Read also:
- Rules of reading in English
- How to quickly learn and memorize English words
- Selection of online English dictionaries and their useful features
Our courses:
